

Machines (EOS M290) at three locations are utilized to create the samples used to obtain bulk material data with metallic materials properties development and standards (MMPDS).
Problem
A major factor driving complexity within additive manufacturing (AM) product qualification and technology adoption is a lack of industrially recognized materials data critical to product design cycles. At present, the absence of prevalent material allowable data requires substantial (usually >$1M and > 18 months) investment prior to any product manufacturing and testing. The material data and models necessary for common design practices require manufacturing, testing, and analysis of hundreds of test coupons using a controlled process. While there are proprietary AM design databases, these dispersed datasets don’t offer the widespread understanding necessary to diminish barriers facing the AM supply chain and inhibit the technology’s prevalence and use.
Objective
The program addresses the lack of industrially recognized, statistically based bulk material allowables using an approach like those commonly utilized in commercial and military aerospace design. Statistically based, bulk material allowables will be delivered utilizing a qualified material and process while leveraging practices informed by government and public advisory groups and mirroring MMPDS allowables generation for cast and wrought metallic materials.
Technical Approach
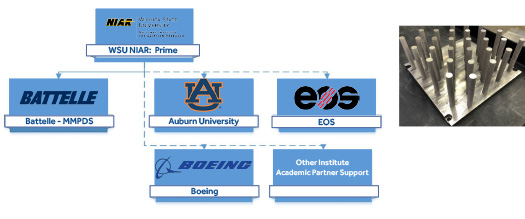
The National Institute for Aviation Research (NIAR) is leading the effort which leverages expertise and resources at Boeing, Auburn University, and Battelle. The approach includes material and process qualification exercises necessary to establish material and process specifications and process control documentation prior to test coupon production. Upon qualification of the Ti-6Al-4V LPBF material and processes, the team will execute a site comparison analysis across multiple production sites at NIAR, Boeing, and Auburn University using various lots of powder feedstock material sourced from multiple suppliers (ATI, AP&C, and Tekna). Common build design factors such as layer timing, coupon spacing, and coupon orientation will be evaluated. Site and process qualification includes density, specific heat capacity, thermal diffusivity, coefficient of thermal expansion, tension, compression, shear, low cycle fatigue, fracture toughness, and hardness testing. T90 and T99 material allowables will be produced upon the conclusion of site qualification for tensile and fatigue properties. Data will be analyzed and procured in a manner in line with MMPDS and the National Center for Advanced Materials Performance (NCAMP) processes to deliver a set of public data which is industrially relevant and statistically substantiated for LPBF Ti-6Al-4V bulk material properties.
Project Participants
Project Principal

Other Project Participants
- Boeing
- Auburn University
- Battelle
Public Participants
- U.S. Department of Defense
