

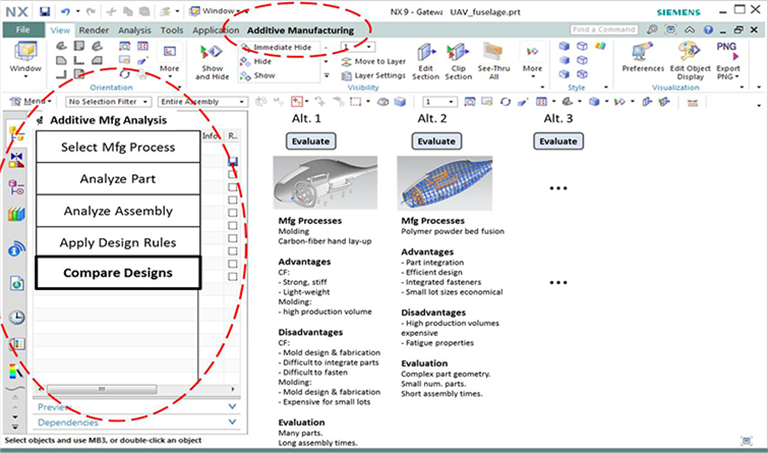
This project addresses gaps in the current additive manufacturing (AM) design-to-print workflow by enabling the insertion of decision tools and AM-aware design tools into Siemens NX CAD system and within the Senvol database.
Problem
Additive manufacturing (AM) part design iteration, analysis, optimization, prototyping and production methods, and tools have all relied on a patchwork of techniques and computer aided design (CAD) data formats which have evolved from conventional material and machining. Training for design engineers to learn how to design components specifically for AM and software tools to facilitate and enhance these designs are needed to fully exploit the advantages of AM.
Objective
The goal of this project is to address gaps in the current AM design-to-print workflow by enabling the insertion of decision tools and AM-aware design tools into an existing CAD system and database. The project seeks to create a comprehensive knowledge base (KB) that codifies good design practices; a web-based portal that educates designers on design for AM (DFAM) and provides guidance on process capabilities and limitations; a suite of CAD-integrated design-for-manufacture tools; a methodology enabling accurate finite element analysis (FEA) modeling coupled with process parameter variables; and DFAM course materials for technical colleges and universities.
Technical Approach
The DFAM knowledge and corresponding web-based portal is being compiled for both powder bed fusion (PBF) and fused deposition modeling (FDM) technologies. CAD-integrated design tools include DFAM analysis and design exploration tools for lattice structure generation, topology optimization, and part consolidation developed for both polymer and metal technologies. Finally, an anisotropic and dynamic process, coupled with material characterization, is being developed for the FDM technology. Relevant process variables, such as localized toolpath direction and void content, are being generated within the DFAM ecosystem for input in the creation of a part specific FEA material model.
Accomplishments
The feature capability and mechanical property characterization activities yielded extensive information about FDM and polymer PBF parts that can benefit many AM users and designers. By populating the knowledge base with this information, software tools were developed so that designers can browse the data and integrate the KB with the NX CAD system. This allowed the feature capability and mechanical property information to be available in the AM-aware tools, effectively enabling the tools to become AM-aware. Additionally, the information provided the foundation for the machine and material selection tool. The industry partners saw great value in these activities and the results that were generated.
More broadly, the information obtained was used to populate the knowledge base, provided the results for the on-line DFAM tutorial, supplied the selection and CAD tools already described, and assisted in the development of education materials. The DFAM tutorial is a publicly accessible web site where users can learn about FDM and polymer PBF feature capabilities and mechanical properties. Project results and DFAM lessons learned from the project played a major role in the development of materials for the industry short courses, as well as the university DFAM course materials. Furthermore, understanding of DFAM from the project contributed to the development of three international ISO/ASTM standards on design guidelines for AM.
Project Participants
Project Principal

Other Project Participants
- Siemens
- MSC Software
- Senvol
- Stratasys
- University of Texas-Austin
- University of Texas-Arlington
- Lockheed Martin
- GKN
- Woodward
- Northrop Grumman
- Rockwell Collins
- Textron Aviation
- General Motors (GM)
Public Participants
- U.S. Department of Defense
- National Science Foundation
- U.S. Department of Energy
